All About Mold and Mildews: Signs, Causes, Impacts, Elimination

Mold growth is the development of microscopic fungi that thrive in damp, humid, and poorly ventilated environments, while mildew growth is a specific type of mold that thrives on flat, moist surfaces and typically appears as a powdery or downy layer. Mold and mildew are two different scenarios. The starting stage of the mold is considered as mildew. So both of them require the same conditions to grow and spread on the surface.
Mold and mildews has different colors and different types. Mold and mildew growth can be identified by the musty odor, discolorations, stain marks, paint peeling, paint bubbling, warped or swelling dry wall, allergy symptoms, and dark patches behind the furniture and appliances.
Higher humidity above 60%, temperature between 77-86°F (25-30°C), lack of ventilation, darkness, and organic matter are the essential environmental conditions for the mold. The mold growth increased by the organic surface, prolonged dampness, lack of sunlight, and poor ventilation.
When mold and mildew growth is prolonged, it causes to reduce the structural strength, decreases indoor air quality, lowers property value, causes insulation problems, damages the finishings, and increases the health risk of the homeowners. In order to prevent this, Aqviz experts always recommend DIY solutions first.
You can use white vinegar, hydrogen peroxide, baking soda, tea tree, borax, and install
dehumidifier in the area. These DIY solutions help to remove mold quickly and are highly recommended for the beginning stages. If the mold is large, contact a mold remediation service. But we highly recommend that you install a waterproofing membrane on the infected area. It is the permanent and the best lifetime solution.
What is Mold Growth?
The definition of mold growth is the development of microscopic fungi that thrive in damp, humid, and poorly ventilated environments. Mold appears in various colors, such as black, green, white, orange, or even pink, depending on the species. The most commonly encountered indoor mold types include Cladosporium, Penicillium, Aspergillus, and Stachybotrys chartarum (often called black mold). Mold forms in colonies and spreads over porous surfaces like drywall, insulation, wood, or fabric.
Mold growth is increased by dampness, darkness, organic surfaces, and poor ventilation in the home. Mold not only causes surface discoloration and foul odors, but also deteriorates structural materials, reducing the integrity of drywall and wood. More than that, mold growth can trigger serious health issues, including allergic reactions, asthma, and other respiratory problems.

What is Mildew Growth?
The definition of mildew growth is a specific type of mold that thrives on flat, moist surfaces and typically appears as a powdery or downy layer. Mildew forms during the early stages of mold development in areas with limited air circulation and consistent humidity levels above 60%. The most common mildew varieties in the home are Oidium and Peronospora. These meldew can be observed as white, gray, or yellowish shades that darken over time. Mildews can be seen on bathroom tiles, shower curtains, basement walls, and painted woodwork where condensation or water seepage occurs.
Mildew spreads quickly on organic materials and can degrade painted surfaces, wallpaper, drywall, and textiles. As well as mildew growth causes not only aesthetic damage like staining and surface discoloration, but also contributes to a musty odor and potential allergic reactions in sensitive homeowners.
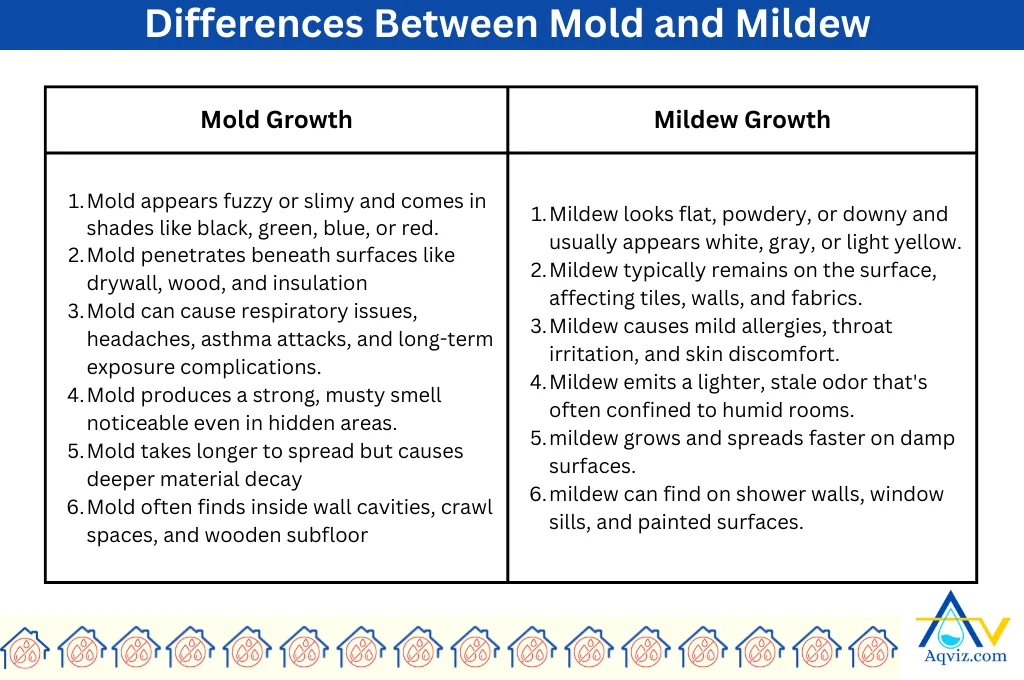
What are the Differences Between Mold and Mildew?
Mold and mildew growths are two different scenarios. Below are the key and minor differences between mold and mildew.
Appearance, Depth of Penetration, and Health Risk Differences between molds and mildews.
Appearance: Mold appears fuzzy or slimy and comes in shades like black, green, blue, or red, while mildew looks flat, powdery, or downy and usually appears white, gray, or light yellow.
Depth of penetration: Mold penetrates beneath surfaces like drywall, wood, and insulation, while mildew typically remains on the surface, affecting tiles, walls, and fabrics.
Health risks: Mold can cause respiratory issues, headaches, asthma attacks, and long-term exposure complications, while mildew causes mild allergies, throat irritation, and skin discomfort.
Odor, growth rate, and breeding surface differences between molds and mildews.
Odor: Mold produces a strong, musty smell noticeable even in hidden areas, while mildew emits a lighter, stale odor that’s often confined to humid rooms.
Growth rate: Mold takes longer to spread but causes deeper material decay, while mildew grows and spreads faster on damp surfaces.
Breeding surface: Mold often finds inside wall cavities, crawl spaces, and wooden subfloor, while mildew can find on shower walls, window sills, and painted surfaces.
What are the Signs of Mold and Mildew Presence?
The signs of mold and mildew presence help detect early signs of mold and mildew. It helps to prevent structural damage and health risks in the early stages. So these are the six common signs of mold and mildew in the home.
- Musty odor: Mold produces a strong, earthy smell typically concentrated in basements, crawl spaces, and behind drywall.
- Discoloration or staining: Mold and mildews are black, green, or gray blotches appearing on walls, ceilings, tile grout, and wood surfaces.
- Peeling or bubbling paint: Mold and mildew, and extreme moisture can peel the paint and bubble over time. This can be seen in bathrooms, kitchens, and basement walls, where moisture pushes the paint away from the substrate.
- Warped wood or swelling drywall: Mold and mildew can be found in floorboards, baseboards, and wall panels near plumbing lines or roof leaks.
- Allergy symptoms indoors: Molds and mildews can cause sneezing, coughing, or skin irritation in humans. If you see these symptoms, it can be a mold sign in the home.
- Dark patches behind furniture or appliances: Mold color is visible as dark patches, especially in kitchens and bathrooms, where airflow is limited and moisture builds up unnoticed.
Read More About: 8 Severe Water Damages in the Home: Causes, Impacts, Preventions

What are the Causes of Mold and Mildew Growth?
At Aqviz, we’ve identified the six most common causes that lead to mold and mildew growth in residential structures.
- Water seepage through foundation walls and concrete slabs
- Plumbing leaks in bathrooms, kitchens, and behind drywall
- Poor ventilation in enclosed areas like attics, crawlspaces, and basements
- High indoor humidity levels above 60% in living areas and laundry rooms
- Roof leaks from damaged flashing, gutters, or shingles
- Condensation on cold surfaces such as windows, metal ducts, and uninsulated walls
What are the Environmental Conditions for Molds?
These are the 5 helpful environmental conditions for the molds.
- High moisture and humidity Level above 60%
- Temperature between 77-86°F (25-30 ° C)
- Lack of ventilation
- Darkness
- Organic matters

What are the Impacts of Mold and Mildew Growth?
Mold and mildew growth can severely affect both indoor air quality and structural integrity. So, below are the most common 6 negative impacts of mold and mildew growth in the home.
- Reduce the structural strength of porous building materials like drywall, wood framing, and OSB sheathing by feeding on organic components and causing decay.
- Decrease indoor air quality by releasing spores and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that trigger respiratory problems, asthma, and skin irritations.
- Lost property value due to visible staining, strong odors, and buyer concerns over hidden water damage and fungal contamination.
- Compromise insulation performance in walls and attics where mold and mildew grow on fiberglass batts and cellulose materials, leading to higher energy bills.
- Damage finishes and surfaces by causing paint to peel, wallpaper to bubble, and surfaces to stain, especially in basements, bathrooms, and laundry rooms.
- Increase health risks for infants, elders, and immunocompromised individuals by promoting chronic sinus infections, allergic reactions, and breathing difficulties.

In Which Areas Does Mold and Mildew Grow?
At Aqviz, we’ve treated thousands of homes affected by mold and mildew, and we consistently see these fungi targeting the same high-risk areas. Below are the top five areas where mold and mildew commonly grow.
Basements: Mold and mildew can grow in the basement due to poor ventilation and water seepage through concrete or block foundations. Basement mold growth is encouraged by the organic dust and stored cellulose-based materials like cardboard boxes and wood.
Bathrooms: Mold growth can be seen in bathrooms due to high humidity from hot showers and inadequate exhaust ventilation. The mold growth rate in the bathroom is increased due to higher moisture, wood, drywall, and painted surfaces.
Attics and ceiling: Mold can be seen in the attic area and the ceiling due to improper insulation, condensation, organic surfaces like wood rafters, sheathing, and blown-in insulations.
Read More About: All About Ceiling Mold: Types, Causes, and Removal
Kitchens: Mold growth can be seen in kitchens due to leaky sink plumbing and steam buildup supports growth on cabinet interiors and MDF (medium-density fiberboard) surfaces.
Laundry rooms: Mold growth occurs in laundry rooms due to higher moisture levels. Moisture from washers and dryer vents, especially in unfinished utility spaces, creates ideal conditions for growth on drywall and unsealed wood.

How Aqviz Eliminates Mold and Mildew?
Aqviz recommends that homeowners to follow the following six DIY methods to eliminate visible growth, especially on non-porous surfaces.
- White vinegar spray: Apply undiluted white vinegar directly onto moldy tile, glass, or metal. Let it sit for one hour, then scrub and rinse.
- Hydrogen peroxide solution: Use 3% hydrogen peroxide in a spray bottle to treat mildew on bathroom walls and ceilings. It disinfects and breaks down fungal roots.
- Baking soda paste: Mix baking soda with water and apply on the moldy grout lines and tile. Scrub with a brush to lift spores and residue.
- Tea tree oil mix: Combine 1 teaspoon of tea tree oil with 1 cup of water. Spray in closets, under sinks, and on bathroom walls to kill mold and mildew.
- Borax solution: Mix 1 cup of borax with 1 gallon of water. Use it to clean drywall, wood trim, and painted surfaces without rinsing. It helps to prevent mold regrowth.
- Use dehumidifiers and ventilation : Use dehumidifiers in highly condensed areas. It helps to lower the indoor humidity and prevent mold growth in the area.
Read More: 10 Ways to Stop Severe Water Damage in the House

If these DIY methods fail or if mold and mildew return quickly, we at Aqviz recommend four advanced mold remediation approaches.
- Use a professional mold remediation service.
- Use HEPA vacuuming and the negative air pressure method for large contaminated areas.
- Replace porous material surfaces like drywall and insulation.
- Install a waterproofing membrane , which we consider the most effective and permanent solution for eliminating moisture at its source
How to Prevent Mold and Mildew Growth?
Homeowners can avoid fungal growth by following proven moisture control practices and maintaining a dry, well-ventilated home environment.
- Fix plumbing leaks immediately in kitchens, bathrooms, and laundry areas to eliminate water sources.
- Improve ventilation in high-humidity areas like bathrooms, basements, and attics using exhaust fans and vented soffits.
- Use dehumidifiers to maintain indoor humidity below 50%, especially in crawlspaces, cellars, and moisture-prone rooms.
- Seal cracks in foundation walls and concrete floors using professional-grade waterproofing membranes like bituminous coatings or polyurethane sealants.
- Insulate cold surfaces such as water pipes, HVAC ducts, and basement walls to prevent condensation and fungal growth.
- Clean and maintain gutters and downspouts to direct rainwater away from the foundation and prevent seepage.
- Install vapor barriers in crawlspaces and basements to block ground moisture from entering the living space.
How to Stop Water Damage in the House?
Stopping water damage in the house starts with moisture control and long-term waterproofing strategies. Aqviz experts always recommend that you to follow these 7 ways to stop these severe water damages in the house.
- Apply cementitious waterproofing, polyurethane coatings, or HDPE membranes to block seepage through basement walls and footings.
- Maintain gutters, extend downspouts at least 6 feet (1.8 meters) away, and fix damaged shingles and flashing to prevent roof leaks.
- Use a battery backup sump pump system in flood-prone basements to remove rising groundwater efficiently.
- Ensure soil slopes away from the foundation at a minimum of 2% over the first 10 feet (about 2.4 meters) to direct rainwater away.
- Replace corroded pipes, dripping faucets, and faulty appliances like dishwashers or washing machines that can silently leak.
- Use epoxy or silicate-based sealants on concrete walls to block capillary moisture transfer in finished basements.
- Keep indoor levels below 50% with dehumidifiers and ventilation systems to stop condensation-related water buildup.
