6 Types of EPDM Waterproofing Membranes, Thickness, Usage, Pros and Cons

EPDM waterproofing membranes are available as mainly 6 different types according to their material composition, performance, thickness, and usage. These are the most used 6 types of EPDM waterproofing membranes such as
- Reinforced EPDM Waterproofing Membrane
- Non-Reinforced EPDM Waterproofing
- Self-Adhesive EPDM Waterproofing
- Mechanically Fastened EPDM Waterproofing
- Ballasted EPDM Waterproofing Membrane
- White EPDM Waterproofing Membrane
Aqviz experts have prepared this guide, including all the details about EPDM waterproofing by considering the above properties, which are essential for the homeowners. We recommend you to use this guide before selecting an EPDM waterproofing for your home improvement project.
1. Reinforced EPDM Waterproofing Membrane
Reinforced EPDM waterproofing membranes are composed of EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) rubber that is internally reinforced with a polyester fabric scrim. This reinforcement enhances puncture resistance, tensile strength, and dimensional stability, making it ideal for high-traffic areas and mechanically fastened applications. Unlike non-reinforced EPDM, the polyester reinforcement prevents excessive stretching and maintains structural integrity under extreme weather conditions.
Reinforced EPDM membranes are available in 45-mil (1.14 mm), 60-mil (1.52 mm), and 75-mil (1.90 mm) thicknesses.
Before you install Reinforced EPDM waterproofing membrane, you should read this important guide. It includes all about EPDM Waterproofing and its includes all details about the definition, properties, test methods, usage, installing, and protection
Common Uses of Reinforced EPDM Waterproofing Membranes
- Commercial and industrial flat roofs
- Mechanically attached roofing systems
- Metal roof retrofits
- Waterproofing for high-wind areas
- Roofs with heavy foot traffic
Pros of Reinforced EPDM Waterproofing Membranes
- High puncture resistance: Reinforced EPDM waterproofing withstands heavy foot traffic and equipment loads.
- Better dimensional stability: Reinforced EPDM waterproofing resists shrinking and stretching over time.
- Stronger wind uplift performance: Reinforced EPDM waterproofing is ideal for mechanically fastened systems.
- Superior tear strength: Reinforced EPDM waterproofing reduces risks of damage during installation and maintenance.
- Longevity and durability: Reinforced EPDM waterproofing is designed for long-term performance in extreme weather conditions.
Cons of Reinforced EPDM Waterproofing Membranes
- Higher cost: Reinforced EPDM waterproofing is more expensive than non-reinforced EPDM due to added reinforcement.
- Less flexibility: Reinforced EPDM waterproofing is harder to stretch and mold around complex roof shapes.
- Heavier weight: Reinforced EPDM waterproofing can be more challenging to install compared to non-reinforced versions.
- Requires specialized installation: Reinforced EPDM waterproofing needs proper fastening and seam sealing techniques.
- More seams required: Reinforced EPDM waterproofing typically comes in smaller sheet sizes than non-reinforced EPDM.
Read more about these 10 Types of Waterproofing Membranes if you wish to use another waterproofing method rather than EPDM.

2. Non-Reinforced EPDM Waterproofing Membrane
Non-reinforced EPDM waterproofing membranes are flexible, single-ply rubber sheets made purely of EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) material without any internal reinforcement. Non reinforced EPDM membranes are highly elastic, allowing it to stretch and conform to irregular surfaces, making it a preferred choice for fully adhered and loose-laid applications. Due to its high elongation (up to 465%), it can accommodate structural movements, thermal expansion, and substrate shifts without tearing or cracking.
Non-reinforced EPDM membranes are available in 45-mil (1.14 mm), 60-mil (1.52 mm), and 90-mil (2.29 mm) thicknesses, with thicker versions offering enhanced durability and longer lifespan.
Common Uses of Non-Reinforced EPDM Waterproofing Membranes
- Fully adhered roofing systems
- Waterproofing terraces and balconies
- Green roofs and planter boxes
- Basement and foundation waterproofing
- Complex roof designs with many penetrations
Pros of Non-Reinforced EPDM Waterproofing Membranes
- Superior flexibility: Non-Reinforced EPDM Waterproofing conforms easily to irregular surfaces and penetrations.
- Easier to install: Non-Reinforced EPDM Waterproofing is lightweight and requires minimal seam fastening.
- Seamless appearance: Non-Reinforced EPDM Waterproofing can be installed in large sheets to reduce seams.
- Ideal for waterproofing details: Non-Reinforced EPDM Waterproofing is best for flashing, expansion joints, and curved structures.
- Long lifespan: Non-Reinforced EPDM Waterproofing can last over 30 years with proper installation and maintenance.
Cons of Non-Reinforced EPDM Waterproofing Membranes
- Lower puncture resistance: Non-Reinforced EPDM Waterproofing is more vulnerable to tears and mechanical damage.
- Not suitable for high-traffic areas: Non-Reinforced EPDM Waterproofing can wear down faster under foot traffic.
- Requires adhesive bonding: Non-Reinforced EPDM Waterproofing needs a strong adhesive to prevent movement.
- More prone to shrinkage: Non-Reinforced EPDM Waterproofing can shrink slightly over time if not properly adhered.
- Limited wind uplift resistance: Non-Reinforced EPDM Waterproofing is less suitable for mechanically fastened applications.

3. Self-Adhesive EPDM Waterproofing Membrane
Self-adhesive EPDM waterproofing membranes, also known as SA EPDM membranes, come with a factory-applied pressure-sensitive adhesive (PSA) backing that eliminates the need for traditional bonding adhesives. This innovation significantly reduces installation time, labor, and solvent-related odors. The membrane is typically a non-reinforced EPDM sheet with a pre-applied adhesive layer, making it an excellent choice for projects requiring a fast, clean, and efficient waterproofing solution.
Self-adhesive EPDM membranes are available in 60-mil (1.52 mm) thickness and commonly supplied in 10′ x 100′ (3m x 30m) rolls.
Common Uses of Self-Adhesive EPDM Waterproofing Membranes
- Low-slope commercial and residential roofs
- Waterproofing over existing substrates (retrofits)
- Green roofs and terraces
- Roofing in environmentally sensitive areas (solvent-free)
- Waterproofing near occupied buildings where fumes are a concern
Pros of Self-Adhesive EPDM Waterproofing Membranes
- Fast and easy installation: Self-Adhesive EPDM Waterproof membranes require no adhesives to mix or apply separately.
- Solvent-free and low odor: Self-Adhesive EPDM Waterproof membranes are ideal for schools, hospitals, and enclosed spaces.
- Strong and uniform adhesion: Self-Adhesive EPDM Waterproof membranes securely bond across the entire surface.
- Cold-weather installation: Self-Adhesive EPDM Waterproof membranes can be installed at temperatures as low as -7°C (20°F).
- Fewer materials needed: Self-Adhesive EPDM Waterproof membranes eliminate the need for additional adhesives and primers in most cases.
Cons of Self-Adhesive EPDM Waterproofing Membranes
- Higher material cost: Self-Adhesive EPDM Waterproof membranes are more expensive than traditional adhered EPDM.
- Limited flexibility during installation: Self-Adhesive EPDM Waterproof membranes, once adhered, are difficult to reposition.
- Requires a clean, dry substrate: Self-Adhesive EPDM Waterproof membranes need a dust-free, moisture-free, and debris-free surface for proper adhesion.
- Not suitable for mechanically fastened systems: Self-Adhesive EPDM Waterproof membranes are designed for adhered applications only.
- Shelf life considerations: Self-Adhesive EPDM Waterproof membranes have a limited storage time due to factory-applied adhesive and require proper handling.

4. Mechanically Fastened EPDM Waterproofing Membrane
Mechanically fastened EPDM waterproofing membranes are designed for wind-uplift resistance and structural stability by securing the membrane to the roof deck using fasteners and seam plates. These membranes are commonly reinforced with polyester fabric to enhance tensile strength and reduce fluttering caused by wind. Unlike fully adhered systems, this installation method allows for faster, more cost-effective application while maintaining durability.
Mechanically fastened EPDM membranes are available in 45-mil (1.14 mm), 60-mil (1.52 mm), and 75-mil (1.90 mm) thicknesses, with thicker options providing added strength and longevity.
Common Uses of Mechanically Fastened EPDM Waterproofing Membranes
- Large commercial and industrial flat roofs
- High-wind zones and hurricane-prone areas
- Metal roof retrofits
- Buildings with lightweight roof decks
- Budget-conscious projects requiring durability
Pros of Mechanically Fastened EPDM Waterproofing Membranes
- Superior wind-uplift resistance: Mechanically Fastened EPDM Waterproofing is ideal for buildings in high-wind zones.
- Faster installation: Mechanically Fastened EPDM Waterproofing requires less adhesive, reducing labor time.
- Lightweight system: Mechanically Fastened EPDM Waterproofing does not add significant load to the structure.
- Good cost efficiency: Mechanically Fastened EPDM Waterproofing is more affordable than fully adhered systems.
- Easy repair and maintenance: Mechanically Fastened EPDM Waterproofing allows for easy membrane replacement if needed.
Cons of Mechanically Fastened EPDM Waterproofing Membranes
- Thermal bridging risk: Mechanically Fastened EPDM Waterproofing fasteners can create energy loss points.
- Potential for membrane flutter: Mechanically Fastened EPDM Waterproofing can experience movement and noise in strong winds.
- More seams required: Mechanically Fastened EPDM Waterproofing uses smaller sheet sizes, resulting in more field seams.
- Substrate-dependent: Mechanically Fastened EPDM Waterproofing requires a deck that can hold fasteners securely.
- Less aesthetically clean: Mechanically Fastened EPDM Waterproofing fasteners and plates may be visible under the membrane.
5. Ballasted EPDM Waterproofing Membrane
Ballasted EPDM waterproofing membranes are one of the most cost-effective and time-efficient roofing solutions. This system involves loosely laying a large EPDM membrane over the roof substrate and then holding it in place with ballast materials, such as river-washed stones or concrete pavers. Unlike adhered or mechanically fastened systems, ballasted EPDM does not require adhesives or fasteners, making it one of the easiest EPDM roofing methods to install.
Ballasted EPDM membranes are available in 45-mil (1.14 mm), 60-mil (1.52 mm), and 90-mil (2.29 mm) thicknesses. Thicker membranes provide better durability and puncture resistance, especially in areas exposed to foot traffic or environmental stress.
Common Uses of Ballasted EPDM Waterproofing
- Large commercial and industrial buildings
- Flat and low-slope roofs
- Green roofs and eco-friendly applications
- Roofs with minimal penetrations
- Budget-friendly waterproofing projects
Cons of Ballasted EPDM Waterproofing
- Quick and easy installation: Ballasted EPDM Waterproofing requires no adhesives or fasteners.
- Low labor costs: Ballasted EPDM waterproofing uses fewer materials and a simplified installation process, reducing costs.
- Energy-efficient: Ballasted EPDM waterproofing provides thermal mass, reducing temperature fluctuations.
- Good resistance to UV and weathering: Ballasted EPDM waterproofing is protected by the ballast layer from direct exposure.
- Environmentally friendly: Ballasted EPDM waterproofing utilizes recyclable materials and minimal chemical use.
Cons of Ballasted EPDM Waterproofing
- Heavy weight: Ballasted EPDM waterproofing requires a strong structural deck to support the ballast load (typically 10-12 lbs/sq. ft.).
- Limited roof slope: Ballasted EPDM waterproofing is not suitable for steep-sloped roofs.
- Difficult repairs and inspections: Ballasted EPDM Waterproofing requires ballast removal to access the membrane.
- Wind resistance concerns: Ballasted EPDM waterproofing is not ideal for high-wind zones unless secured properly.
- Potential vegetation growth: Ballasted EPDM waterproofing may develop moss and weed growth due to organic material in the ballast.
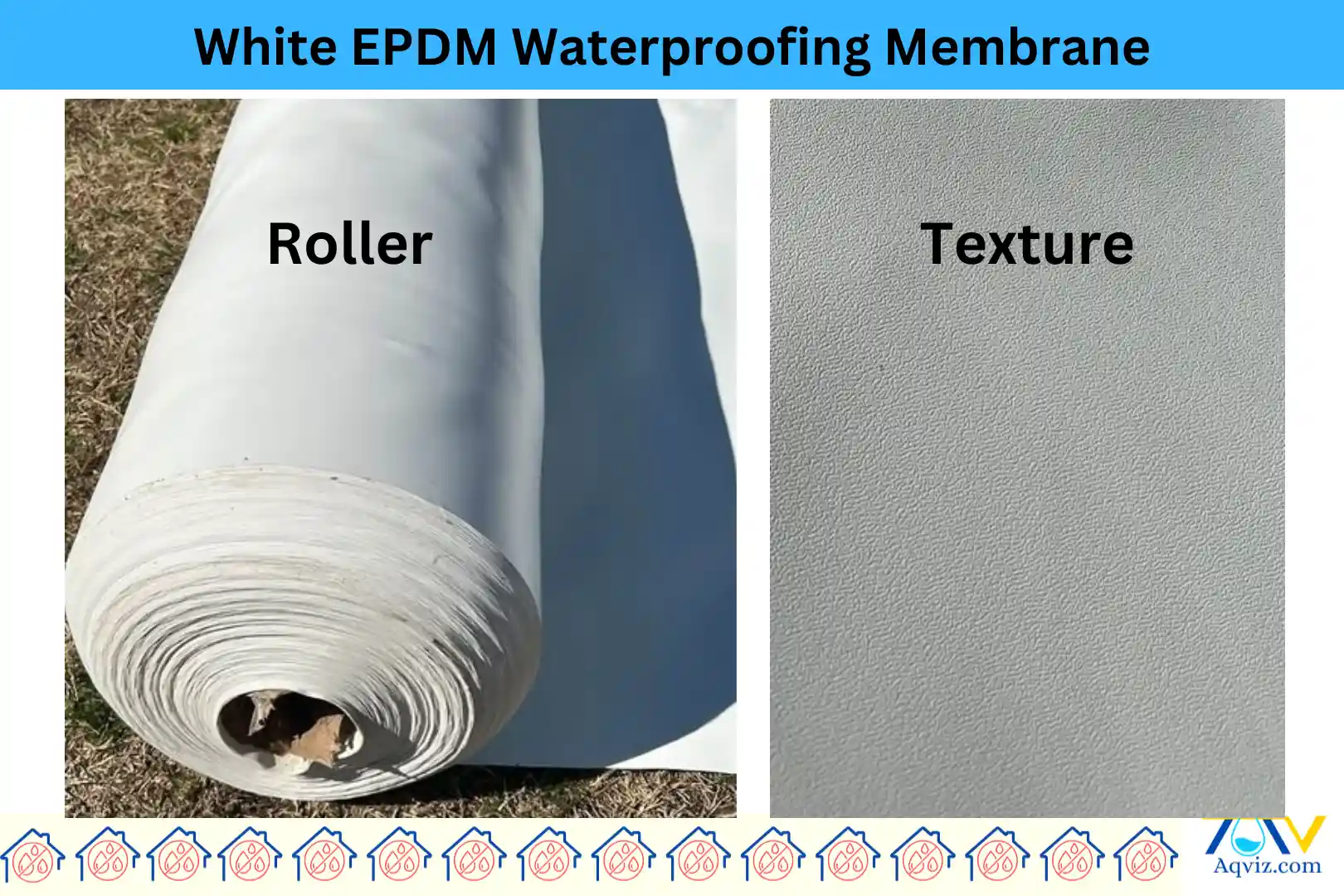
6. White EPDM Waterproofing Membrane
White EPDM waterproofing membranes are a high-performance alternative to traditional black EPDM. White EPDM designed to provide enhanced energy efficiency and reflectivity to the building. White EPDM waterproofing membranes are made from the same Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber. White EPDM features a reflective white surface that helps reduce heat absorption, making it an excellent choice for hot climates and energy-conscious buildings.
This membrane is available in 60-mil (1.52 mm) thickness and typically comes in wide rolls of up to 20′ (6m) x 100′ (30m), reducing the number of seams required during installation.
Common Uses of White EPDM Waterproofing Membrane
- Commercial and industrial low-slope roofs
- Energy-efficient and LEED-certified buildings
- Buildings in warm climates to reduce cooling costs
- Warehouses, data centers, and retail stores
- Sustainable and eco-friendly roofing solutions
Pros of White EPDM Waterproofing Membrane
- High solar reflectivity: White EPDM waterproofing reduces roof temperatures and cooling costs.
- Energy savings: White EPDM waterproofing can lower indoor temperatures by up to 15°F (8°C).
- Meets cool roof standards: White EPDM waterproofing is ideal for buildings seeking LEED certification.
- Durable and long-lasting: White EPDM waterproofing resists UV degradation and extreme weather.
- Same installation methods as black EPDM
Cons of White EPDM Waterproofing Membrane
- Higher material cost: White EPDM waterproofing is more expensive than traditional black EPDM.
- More maintenance required: White EPDM waterproofing is prone to dirt accumulation.
- Reduced heat retention: White EPDM waterproofing is not ideal for cold climates where heating costs are a concern.
- Limited thickness options: White EPDM waterproofing is typically available only in 60-mil thickness.
- Can show seams more visibly: White EPDM waterproofing may highlight seam lines more than black EPDM.
Read More About: What to Know About Roof Waterproofing?
What is the Difference between EPDM and Bituminous Waterproofing?
EPDM and bituminous waterproofing are two of the most common materials used for roof and structure waterproofing, but they differ significantly in composition, performance, installation, and durability. Let’s break down their key differences:
Material Composition Difference between EPDM and Bituminous Waterproofing
- EPDM Waterproofing: Made from Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber, a synthetic single-ply membrane known for its elasticity, UV resistance, and long lifespan. It is available in non-reinforced, reinforced, and self-adhesive options.
- Bituminous Waterproofing: Derived from asphalt or bitumen, often mixed with polymers for flexibility. It comes in different forms such as torch-applied bituminous membranes, self-adhesive bitumen sheets, and liquid-applied bituminous coatings.
Performance Differences between EPDM and Bituminous Waterproofing
- EPDM: Excellent UV and ozone resistance, making it highly durable in direct sunlight and extreme weather conditions. Can last over 30-50 years with proper maintenance.
- Bituminous Waterproofing: Prone to UV degradation, requiring additional protection (such as aluminum foil or gravel cover) to prevent premature aging and cracking. Lifespan is usually around 10-20 years.
Installation Differences between EPDM and Bituminous Waterproofing
- EPDM: Installed using fully adhered, mechanically fastened, or ballasted systems. Some options come with self-adhesive backing, making installation faster and solvent-free.
- Bituminous Waterproofing: Typically applied using heat welding (torch-on method), self-adhesive layers, or liquid applications. Torch-applied membranes require skilled labor and proper safety precautions.
Durability
- EPDM waterproofing membrane can last about 25-30 years while bituminous waterproofing membranes can last about 15-20 years when they are maintained properly.
So which one should you choose?
Here is Aqviz, recommadations.
- If you need long-term durability, superior flexibility, and energy efficiency, EPDM is the better choice, especially for large-scale roofing and green building projects.
- If you have a tight budget and need a cost-effective solution for short to mid-term waterproofing, bituminous membranes may be suitable, but they require more maintenance and may degrade faster.
Read More About: How to Install EPDM Waterproofing Membranes?
Is EPDM Foam Waterproof?
EPDM foam is not completely waterproof like solid EPDM rubber membranes. EPDM foam is a cellular, sponge-like material that comes in open-cell and closed-cell forms. Open-cell EPDM foam has air pockets, making it water-permeable and unsuitable for waterproofing while closed-cell EPDM foam has a denser structure, providing some water resistance, but it is still not ideal for long-term waterproofing.
But EPDM membranes are non-porous sheet that is 100% waterproof, commonly used in roofing, pond liners, and foundation waterproofing.
Is 100% EPDM Closed-Cell Sponge Rubber Waterproof?
100% EPDM closed-cell sponge rubber is highly water-resistant but not completely waterproof in the same way that solid EPDM rubber membranes are. While closed-cell EPDM foam can repel water to a great extent, it may still allow some moisture penetration under prolonged exposure or pressure.
Is EPDM Rubber Waterproof?
Yes, EPDM rubber is 100% waterproof and is widely used for roofing, waterproofing, and sealing applications. It is a synthetic rubber membrane made from Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM), designed to provide superior water resistance in extreme weather conditions.
